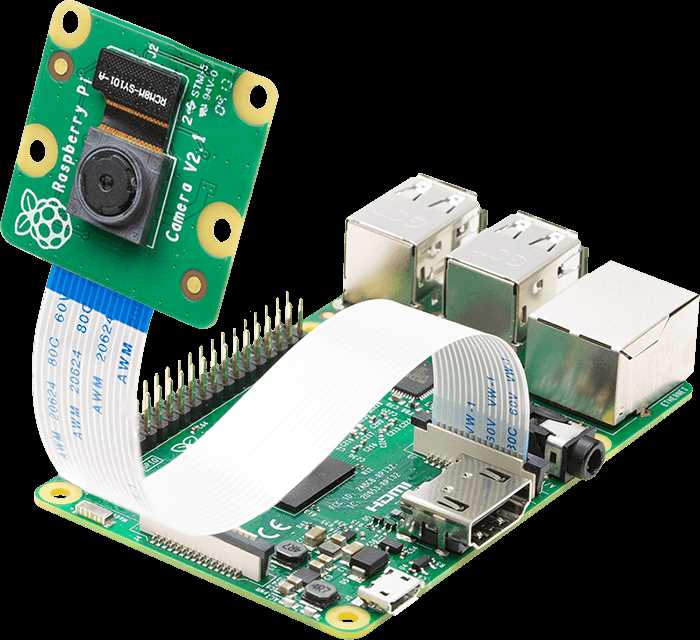

Welcome to the comprehensive guide designed to help you unlock the full potential of your compact computing device. This section will walk you through the essentials of setting up and using your small yet powerful machine, enabling you to seamlessly integrate it into your projects and daily tasks.
Whether you’re an enthusiast eager to dive into the world of micro-computing or a beginner looking to understand the basics, this guide will provide you with the knowledge needed to get started. From initial setup to advanced configurations, you’ll find clear and concise steps to ensure your experience is both informative and enjoyable.
Prepare to explore the fascinating capabilities of your device as we guide you through each phase of the process. By following these instructions, you’ll gain the skills to effectively harness the power of this remarkable tool, opening up a world of possibilities for innovation and creativity.
Getting Started with Raspberry Pi 2
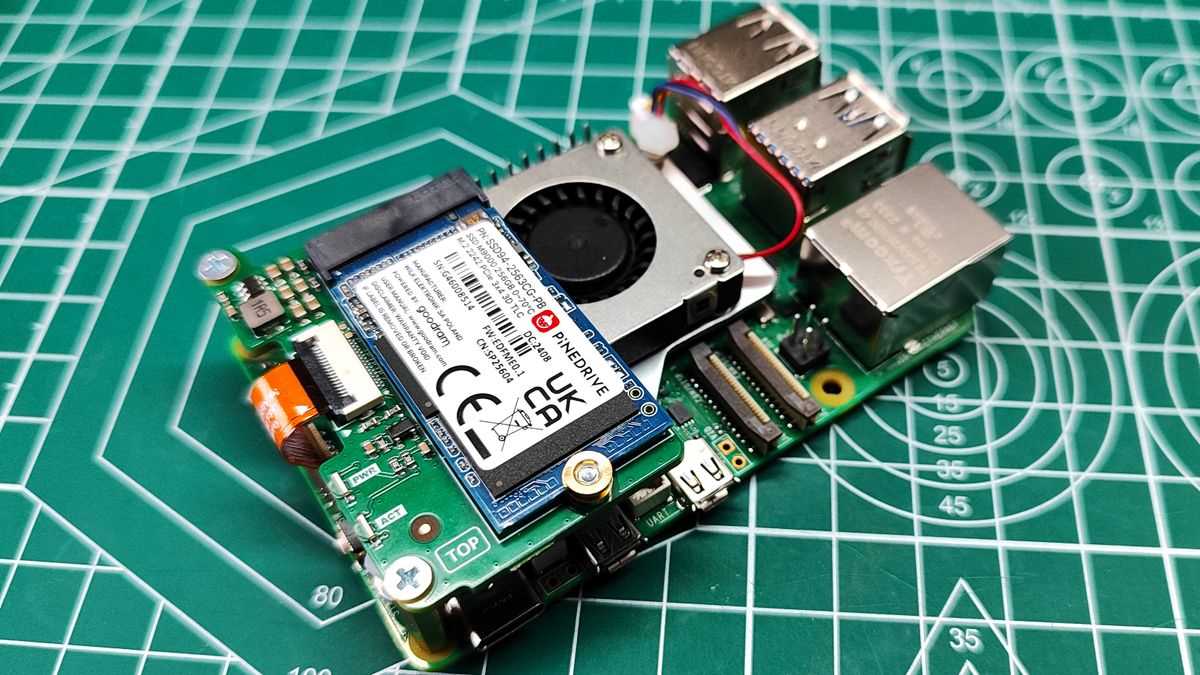

Embarking on your journey with this versatile single-board computer can be both exciting and overwhelming. This guide is designed to help you set up and begin exploring your new device. With a variety of applications and projects possible, understanding the basics of getting started is essential to making the most out of your experience.
Before diving into complex tasks, ensure you have the essential components and accessories. Below is a list of items you will need to begin:
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Supply | Provides the necessary power to the board. Ensure it meets the voltage and current requirements. |
| MicroSD Card | Used for storing the operating system and data. A minimum of 8GB is recommended. |
| HDMI Cable | Connects the board to a monitor or TV for display purposes. |
| Keyboard and Mouse | Input devices needed to interact with the operating system and software. |
| Case | Protects the board from physical damage and dust. |
Once you have gathered these items, follow the steps to set up the device, starting with installing the operating system onto the microSD card and connecting all necessary peripherals. This foundational setup will enable you to explore various functionalities and projects, paving the way for a productive and enjoyable experience.
Overview of Raspberry Pi 2 Features

The second-generation microcomputer offers a range of capabilities designed to enhance computing experiences. This compact device combines powerful processing with a versatile array of connectivity options, making it suitable for a variety of projects and applications. In this section, we will explore the key attributes that contribute to its performance and flexibility.
Performance and Processing Power

At the heart of this board lies a robust central processing unit (CPU) that provides a significant boost in performance compared to its predecessors. Equipped with a multi-core architecture, it allows for smooth multitasking and efficient handling of complex tasks. The enhanced processing power is complemented by increased memory capacity, which supports more demanding applications and faster data access.
Connectivity and Expansion Options
Versatility is a hallmark of this device, evident in its wide range of connectivity features. Users can take advantage of several ports for peripherals and external devices, including USB connectors and an HDMI interface for video output. Networking capabilities are also included, facilitating both wired and wireless connections. Additionally, expansion options via GPIO pins enable users to integrate and control various external components, extending the functionality of the microcomputer to meet diverse needs.
Essential Hardware Components You Need
When setting up a compact computing board, having the right set of hardware is crucial to ensure smooth operation and functionality. Each component plays a specific role in making the device work effectively, from powering it up to enabling connectivity and interaction with other devices. Understanding these key parts helps in assembling a fully functional setup and can greatly enhance the overall experience.
Core Components
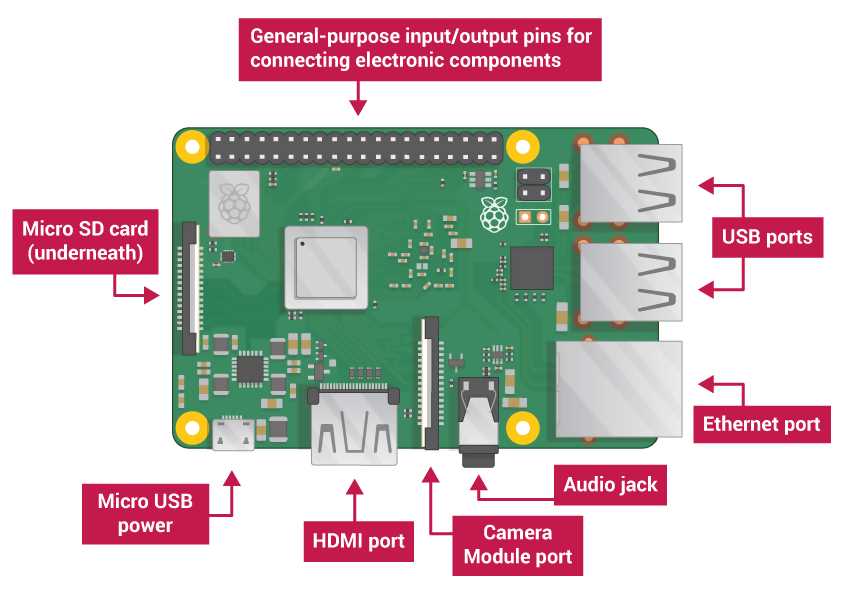
The core components are fundamental to the operation of your computing board. They include the power supply, which ensures that the board receives the correct voltage and current; and the storage medium, which holds the operating system and files. Additionally, a reliable cooling solution may be necessary to prevent overheating during extended use.
Connectivity and Expansion

Connectivity options are essential for interfacing with other devices and peripherals. This includes cables and connectors for display and input devices, such as keyboards and mice. Expansion options, such as additional USB ports and GPIO pins, provide flexibility for adding more functionalities to your setup. Ensuring compatibility between these components and the board is key to a successful configuration.
| Component | Purpose | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Power Supply | Provides necessary power for operation | Ensure voltage and current match specifications |
| Storage Medium | Holds operating system and data | Can be SD card or USB drive |
| Cooling Solution | Prevents overheating | Use heatsinks or fans if needed |
| Display Cable | Connects to monitor or screen | Check compatibility with display |
| Input Devices | Allows user interaction | Includes keyboard and mouse |
Setting Up Your Raspberry Pi 2
Getting your new computing device up and running involves several essential steps. This guide will help you through the process of preparing and configuring your mini-computer, ensuring it is ready for various projects and applications. You’ll start by gathering the necessary components, followed by assembling and powering up your device, and finally, installing the required software.
Gathering Essential Components
Before beginning, ensure you have all the required hardware. You will need a power supply that meets the device’s specifications, a microSD card with sufficient storage, and a compatible display. Additionally, having a keyboard and mouse will aid in navigating the initial setup. Ensure that you also have the appropriate cables to connect everything together.
Assembling and Powering Up

First, insert the microSD card into the designated slot on the device. Connect the display, keyboard, and mouse using the provided ports. After everything is connected, plug in the power supply to boot up the system. The device will initialize, and you will see the startup screen on your display. Follow the on-screen prompts to complete the initial configuration and prepare the system for use.
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to enjoying all the possibilities that your new computing device offers.
Installing and Configuring the Operating System
Setting up the software environment for your compact computing device involves several key steps to ensure smooth operation. This process includes selecting an appropriate system image, writing it to a storage medium, and configuring initial settings to align with your specific needs.
Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the setup:
- Download the OS Image: Begin by obtaining the operating system image from a reliable source. The image file is a snapshot of the OS that will be installed on your device.
- Prepare the Storage Medium: Use an SD card or other compatible storage device. Ensure it has sufficient capacity and is properly formatted to handle the OS image.
- Write the Image to the Storage: Utilize a tool such as
balenaEtcherorRaspberry Pi Imagerto write the OS image to your storage medium. Follow the tool’s instructions for a seamless process. - Insert the Storage into the Device: Once the image writing is complete, place the SD card into the designated slot on the device.
- Power On and Initial Configuration: Connect the device to a power source. Upon booting, you will be prompted to complete initial setup steps such as setting up language preferences, network connections, and user accounts.
- Update and Upgrade: After the initial setup, update the OS to ensure you have the latest features and security patches. Use the terminal to run commands such as
sudo apt-get updateandsudo apt-get upgrade.
By following these steps, you’ll have your compact computing device ready for use, tailored to your preferences and requirements.
Basic Troubleshooting and Maintenance Tips

When working with small computing devices, it’s crucial to know how to address common issues and maintain optimal performance. This section provides practical advice for resolving frequent problems and ensuring your system operates smoothly.
Common Issues and Solutions
- Device Not Booting: If your unit fails to power up, ensure that all connections are secure. Verify that the power supply is adequate and properly connected. Check the SD card for proper insertion and that it is functioning correctly.
- Overheating: Overheating can lead to performance issues. Ensure that the device is placed in a well-ventilated area. Consider using a heatsink or fan to help dissipate heat.
- Unresponsive System: If the system becomes unresponsive, try rebooting the device. If the issue persists, check for software updates or reinstall the operating system to resolve potential software conflicts.
- Network Connectivity Problems: For issues with network connections, check the settings and ensure that cables are properly connected. Restart your router and verify that the network configuration is correct.
Regular Maintenance Tips

- Update Software: Regularly check for and apply software updates to keep the system secure and functioning optimally.
- Backup Data: Frequently back up important data to prevent loss in case of system failures or data corruption.
- Clean Components: Periodically clean the device and its components to prevent dust buildup, which can lead to overheating and hardware damage.
- Check for Loose Connections: Regularly inspect all cables and connectors to ensure they are securely attached and in good condition.
Exploring Advanced Projects and Applications
Venturing into complex projects and practical uses can significantly enhance your understanding and capabilities with single-board computers. These sophisticated endeavors often push the boundaries of what you can achieve with compact, versatile technology. By engaging in such activities, you can uncover new potentials and refine your skills in innovative ways.
One exciting area is home automation, where you can create customized systems to control various aspects of your living environment, from lighting to security. Developing such systems involves integrating sensors, actuators, and communication protocols, allowing for a tailored and efficient management of your home.
Another intriguing application is in the field of robotics. By building and programming robots, you can explore the intricacies of automation, artificial intelligence, and mechanical design. These projects not only offer hands-on experience but also contribute to advancing your knowledge in robotics and related technologies.
Moreover, media centers and entertainment systems represent a popular use case. Crafting your own media center can provide a personalized viewing and listening experience, combining streaming services, local media, and interactive features into a single, cohesive system.
Lastly, engaging in data collection and analysis projects can offer valuable insights into various phenomena. Whether it’s monitoring environmental conditions or conducting experiments, the ability to collect and interpret data in real-time opens up numerous opportunities for exploration and discovery.