
For those with a passion for stargazing and a desire to understand the cosmos, acquiring the right equipment is essential. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of how to start your journey into the night sky. Whether you are a novice or have some experience, this resource will help you maximize your celestial observations.
Understanding Your New Tool is crucial for making the most of your investment. From setting up the device to learning how to locate distant planets and constellations, this guide covers all the basics. It emphasizes practical tips and step-by-step instructions to ensure a smooth experience for first-time users.
Additionally, readers will find detailed advice on fine-tuning settings and selecting the best locations for observation. The aim is to equip enthusiasts with the knowledge needed to explore the wonders of space confidently and effectively.

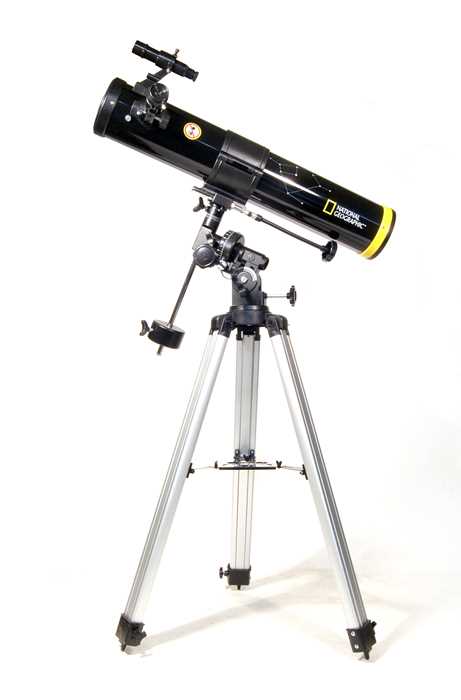
To effectively use any stargazing device, it is crucial to familiarize yourself with its various parts and their purposes. This section will provide a detailed overview of the main components, helping you understand their functions and how they contribute to your overall experience of exploring the night sky.
Main Parts of the Viewing Device

- Optical Tube: The primary structure that houses the lenses and mirrors, essential for gathering and focusing light.
- Eyepiece: The part through which you look to see magnified images. Different eyepieces can offer varying levels of magnification.
- Mount: The supportive frame that holds the device steady. It allows smooth movement and tracking of celestial bodies.
- Finder Scope: A smaller scope attached to the main body, aiding in locating objects before observing them through the main lens.
Additional Accessories and Their Functions
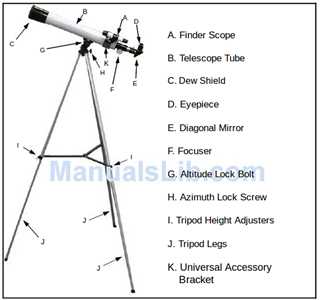
- Tripod: Provides stability, ensuring a
Initial Setup and Alignment

To achieve accurate observations, it is essential to prepare the device properly and ensure it is correctly aligned. This process involves setting up the apparatus in a stable location, followed by fine-tuning its orientation to match the desired celestial coordinates.
- Select a Stable Location: Place the equipment on a flat, sturdy surface to avoid any unwanted movement or vibrations. Ensure that the area is free of obstacles and has a clear view of the sky.
- Assemble the Components: Carefully connect all parts as per the assembly guide, making sure each component is securely attached. Tighten all screws and bolts to ensure stability.
- Level the Base: Use a spirit level to check that the base is perfectly horizontal. Adjust the legs or tripod accordingly to achieve a balanced setup, which is crucial for accurate positioning.
- Initial Alignment: Point the device towards a known reference point, such as Polaris in the Northern Hemisphere. Use the built-in alignment tools to fine-tune the direction and ensure that the device is properly calibrated.
- Calibrate the Optics: Adjust the focus and use the finder scope to center the reference point within the
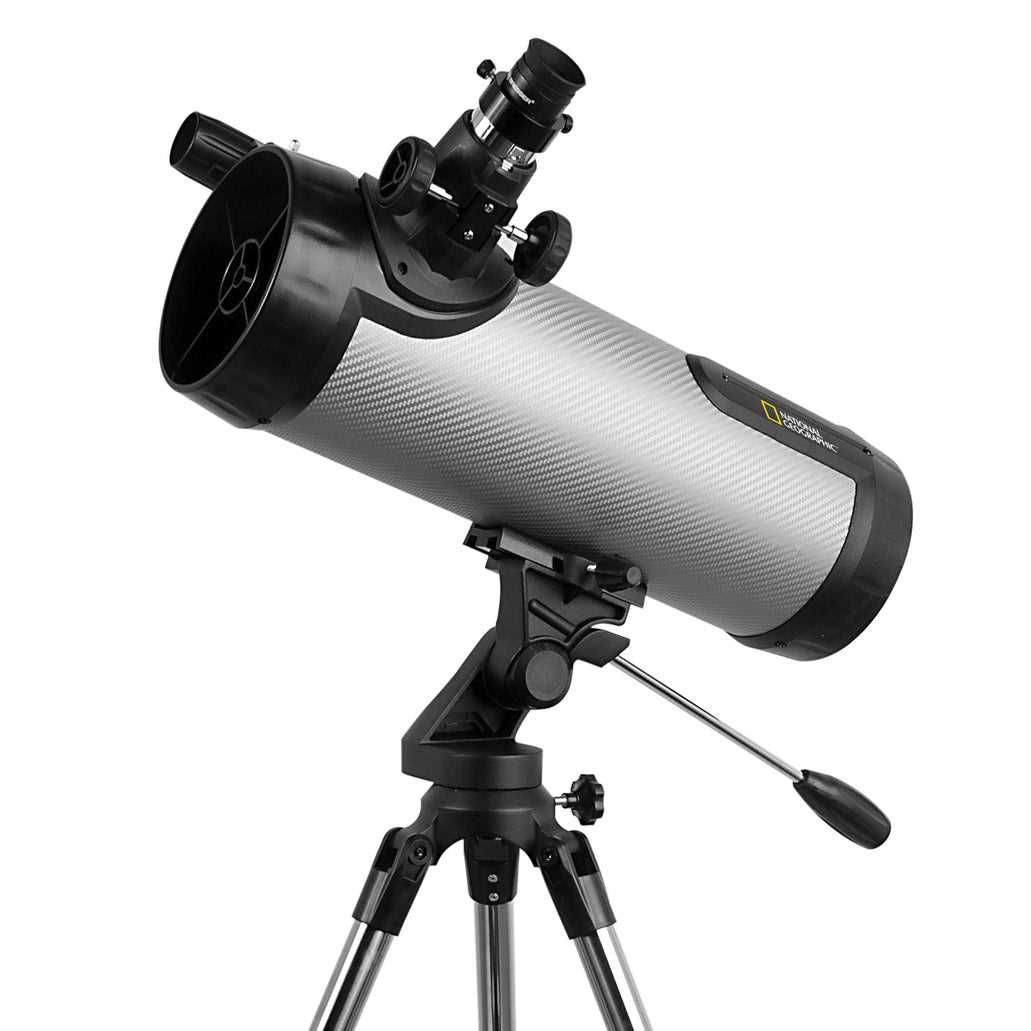
Focusing Techniques for Clear Viewing

Achieving a sharp and detailed image while observing celestial bodies requires a precise approach to focusing. By fine-tuning the adjustment mechanisms, one can enhance clarity and bring distant objects into sharp view. This section will guide you through various methods to achieve optimal focus for an immersive stargazing experience.
Step Technique Description 1 Initial Alignment Begin by roughly aligning the observation instrument with the desired object. Ensure the mount is stable and secure. 2 Coarse Adjustment Use the primary focus control to bring the object into a general focus. This may involve rotating a knob or adjusting a slider, depending on the equipment model. 3 Maintaining Your Telescope for Longevity

To ensure your stargazing equipment remains in optimal condition for years to come, it’s important to follow a few essential maintenance practices. Proper care not only enhances performance but also extends the life of your optical device, allowing for consistent and clear observation of celestial bodies.
Regular cleaning of the lenses and mirrors is crucial to avoid dust accumulation and scratches. Use a soft brush or air blower to remove loose particles, followed by a microfiber cloth to gently clean the surfaces. Never use harsh chemicals or abrasive materials, as they can damage the delicate coatings.
In addition to cleaning, it’s important to store your observation device in a safe environment. A cool, dry place with a protective cover will prevent moisture buildup and potential mold growth. When transporting, use a padded case to protect against impacts and vibrations.
Regular checks of the mechanical parts, such as focusing mechanisms and mounts, are also necessary to ensure smooth operation. Tighten any loose screws and apply a small amount of lubricant to moving parts as needed.
Exploring Astronomical Objects

Observing celestial bodies is a fascinating journey into the vast universe, allowing us to discover the wonders of space. By using an optical device, we can gaze upon distant stars, planets, and other cosmic phenomena, unveiling the mysteries of the night sky. This section will guide you through the exploration of different heavenly bodies, offering insights into what can be seen and how best to observe them.
Planets and Their Features

One of the most captivating targets for beginners and seasoned sky-watchers alike are the planets within our solar system. Each planet presents unique characteristics, from the vibrant bands of Jupiter to the majestic rings of Saturn. Here are some tips on observing planets:
- Choose clear nights when the sky is free from clouds and light pollution.
- Start with the brightest planets, such as Venus and Jupiter, which are easier to spot.
- Use a variety of lenses to get different magnifications and better details.
Stars and Constellations

Stars and their formations, known as constellations, have been used for navigation and storytelling for centuries. Observing these bright points of light can be both educational and awe-inspiring. To better enjoy stargazing:
- Familiarize yourself with major constellations visible in your hemisphere.
- Use a star map
Troubleshooting Common Issues

When using a viewing instrument, encountering problems can be frustrating. This section provides guidance on resolving frequent issues that users might face. Whether it’s related to image clarity, alignment, or mechanical performance, understanding common solutions can enhance your experience.
1. Blurry Images: If the images appear blurry, ensure that the lens or optics are clean. Dust or smudges can impair clarity. Additionally, verify that the focusing mechanism is properly adjusted.
2. Difficulty in Focusing: When focusing seems difficult, check if the focusing knob is functioning smoothly. Sometimes, debris or misalignment can obstruct t