
Keeping track of your blood pressure is a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health. A quality device designed for measuring blood pressure can provide accurate readings, helping individuals monitor their health status effectively. This guide aims to familiarize you with the various features and functions of your device, ensuring you can use it correctly and confidently.
Within this guide, you will find comprehensive information on operating your monitoring device, from setting it up to interpreting the results it provides. By following the instructions carefully, you will gain a better understanding of how to manage your blood pressure readings and make informed health decisions based on the data collected.
Getting Started with Omron BP786N

Setting up your new blood pressure monitor involves a few essential steps to ensure accurate readings and smooth operation. First, familiarize yourself with the device’s components and how they work together. This includes understanding how to properly position the cuff and how to navigate the device’s display and buttons.
To begin, make sure the device is placed on a stable surface and that you are seated comfortably with your arm supported. Follow the instructions for applying the cuff, ensuring it is snug but not too tight. Once the cuff is in place, power on the monitor and follow the on-screen prompts to start the measurement process.
Regular calibration and maintenance are crucial for reliable results. Keep the monitor clean and check the batteries regularly to avoid any interruptions in your monitoring routine. Refer to the guide provided for troubleshooting common issues and to optimize your use of the device.
Unboxing and Initial Setup
Starting with a new device involves several key steps to ensure proper functionality and accuracy. This section outlines the process of unpacking and preparing your new equipment for use.
Begin by carefully removing the device and all included components from the packaging. Verify that all items listed in the enclosed checklist are present. Typically, you will find:
- The main unit
- Power adapter or batteries
- Measurement cuff
- Additional accessories (if applicable)
- Quick start guide
Once all components are confirmed, proceed with setting up the device. This generally involves:
- Inserting batteries or connecting the power adapter
- Attaching the cuff securely to the main unit
- Performing an initial calibration if recommended by the manufacturer
- Testing the device to ensure it powers on and operates correctly
Follow any additional instructions provided in the quick start guide to complete the setup. This will help you familiarize yourself with the basic functions and prepare the device for accurate readings.
Understanding the Device Features
Grasping the capabilities of a blood pressure monitoring device is essential for effective use. These devices come with a variety of features designed to enhance accuracy, convenience, and user experience. Understanding these features can help users make the most of their health monitoring routines.
- Measurement Accuracy: Modern devices are equipped with advanced sensors and algorithms to ensure precise readings. This feature is crucial for tracking health trends and making informed decisions.
- User-Friendly Display: The display often features large, easy-to-read numbers and symbols, which simplifies data interpretation. Some models even offer color-coded results to quickly indicate blood pressure levels.
- Multiple User Profiles: Many devices allow multiple users to store their readings separately. This is particularly useful in households where more than one person uses the device.
- Memory Storage: Devices typically have memory functions to store previous measurements. This feature helps in tracking changes over time and facilitates more detailed health assessments.
- Automatic Cuff Inflation: Automatic inflation features ensure consistent and comfortable measurements without requiring manual adjustment of the cuff.
- Irregular Heartbeat Detection: Some models can detect irregular heartbeats during measurements, providing additional health insights and alerts.
- Data Connectivity: Advanced devices offer connectivity options such as Bluetooth or USB, allowing data to be synced with mobile apps or computers for more comprehensive tracking.
Familiarizing yourself with these features enables you to utilize the device more effectively, ultimately supporting better health management.
Buttons and Display Explained
Understanding the functionality of buttons and the display panel is crucial for effective usage of your device. Each button and display element plays a distinct role in operating and configuring the system, making it essential to familiarize yourself with their functions.
The buttons on the device are designed to control various features and settings. Typically, these include options for power, memory recall, and mode selection. Each button is intuitively placed to ensure easy access and operation.
The display serves as the interface for visual feedback. It shows important information such as measurements, settings, and error messages. The clarity of the display helps users quickly interpret the data and understand the device’s status.
By exploring these components, users can effectively manage the device and enhance their overall experience.
How to Take Accurate Measurements
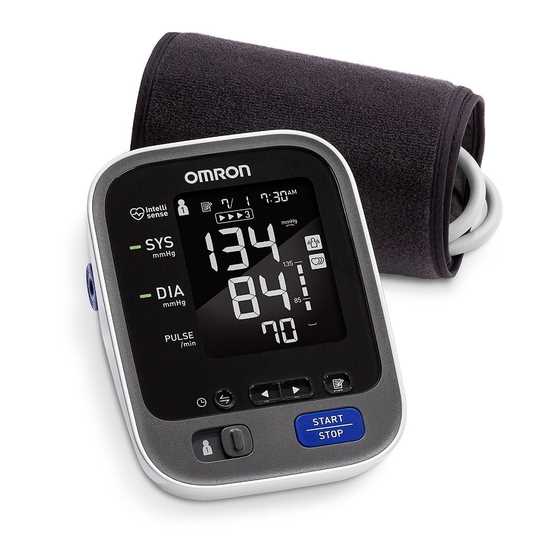
To ensure precise readings, following proper procedures is essential. Adhering to specific guidelines can help avoid common errors and obtain reliable results.
- Positioning: Sit comfortably with your back supported and feet flat on the floor. Rest your arm on a table at heart level, keeping it relaxed.
- Preparation: Ensure the device is correctly calibrated and the cuff is appropriately sized. Wrap the cuff snugly around your upper arm, avoiding any clothing underneath.
- Timing: Take measurements at the same time each day to maintain consistency. Avoid taking readings immediately after physical activity or consuming caffeine.
- Measurement: Remain still and silent during the measurement process. Follow the device’s prompts to ensure accurate results.
Step-by-Step Measurement Guide
This section provides a comprehensive approach to accurately taking measurements with your blood pressure device. Follow the outlined steps to ensure precise readings and optimal performance of your device.
First, position yourself comfortably and ensure that your arm is supported at heart level. Wrap the cuff around your upper arm, making sure it is snug but not too tight. Activate the device and remain still while it calibrates and measures your blood pressure. Review the displayed results to assess your readings accurately.
Interpreting Your Results
Understanding the readings from your blood pressure monitor is crucial for managing your health effectively. These measurements provide insight into your cardiovascular status and can help in detecting potential issues early on. It’s important to interpret these values correctly to make informed decisions about your well-being.
The following table outlines common blood pressure categories and their typical implications:
| Category | Systolic (mm Hg) | Diastolic (mm Hg) | Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | Below 120 | Below 80 | Generally considered healthy; continue with regular monitoring. |
| Elevated | 120-129 | Below 80 | Monitor lifestyle changes; consult a healthcare provider if necessary. |
| Hypertension Stage 1 | 130-139 | 80-89 | Consider lifestyle modifications and seek medical advice. |
| Hypertension Stage 2 | 140 or higher | 90 or higher | Consult with a healthcare provider immediately for treatment options. |
| Hypertensive Crisis | Higher than 180 | Higher than 120 | Seek emergency medical attention right away. |
By regularly reviewing your results and understanding their implications, you can better manage your health and make necessary adjustments to your lifestyle or treatment plan. Always consult with a healthcare professional for personalized advice.
Reading the Blood Pressure Readings
Understanding blood pressure readings is essential for monitoring cardiovascular health. Blood pressure is typically measured in two values: systolic and diastolic pressure. Systolic pressure, the higher number, reflects the force of blood against artery walls when the heart beats. Diastolic pressure, the lower number, represents the force when the heart is at rest between beats.
Interpreting the Results

Blood pressure readings are categorized into different ranges. Normal readings are generally below 120/80 mmHg. Readings between 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic are considered elevated. Hypertension is diagnosed when readings are consistently above 130/80 mmHg.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Several factors can impact the accuracy of blood pressure measurements, including the position of the arm, the fit of the cuff, and the timing of the measurement. It is important to follow proper measurement techniques to ensure reliable results.