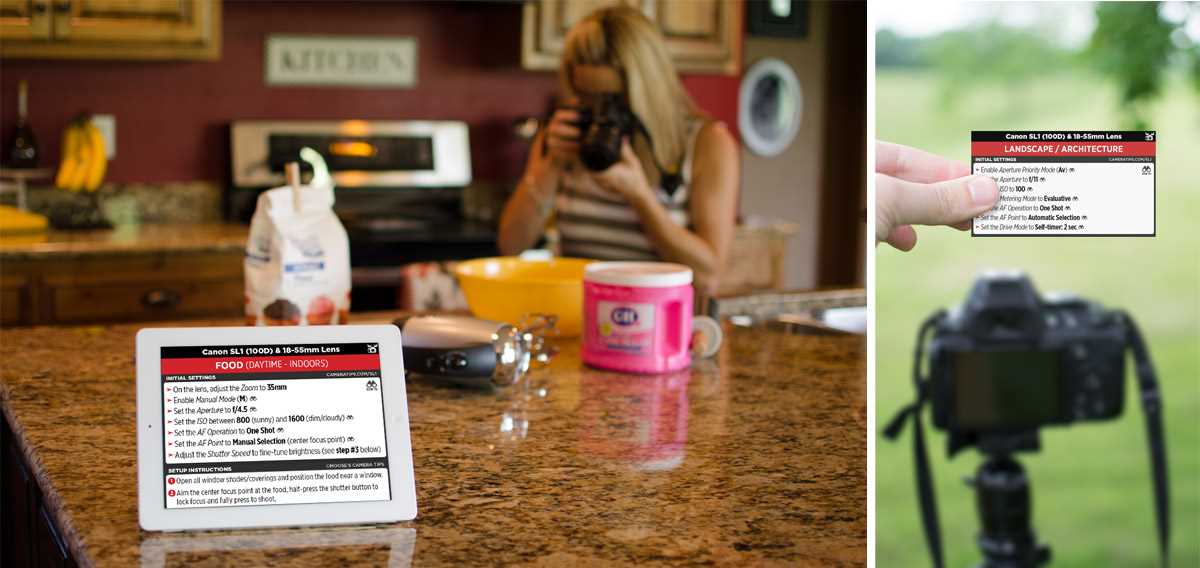

For anyone looking to get the most out of their entry-level digital single-lens reflex camera, understanding its features and functionalities is essential. This guide serves as a detailed resource for navigating the various settings and options available on your new device, ensuring you can capture high-quality images with ease.
Whether you’re new to photography or just transitioning from another camera system, this resource is designed to provide clear and practical advice. It covers everything from basic operations to advanced techniques, helping you harness the full potential of your equipment.
With step-by-step instructions and expert tips, this guide will help you become proficient in using your camera, allowing you to take stunning photos and videos. Explore the features, learn the terminology, and start your journey towards mastering your camera today.
Overview of Canon Rebel SL1 Features

This section provides an overview of the key functionalities and features of the compact DSLR model. Designed to cater to both beginners and enthusiasts, this camera offers a range of tools and settings that enhance the photography experience. Understanding these features will help users make the most of their device, whether for casual shots or more advanced photographic projects.
Key Specifications

- High-resolution imaging with a 18-megapixel sensor
- Fast and responsive autofocus system
- Intuitive touchscreen interface for easy navigation
- Compact and lightweight design for portability
- Various shooting modes including manual control
Advanced Capabilities

- Full HD video recording with customizable settings
- Built-in Wi-Fi for quick sharing and remote control
- Multiple scene modes and creative filters
- High-speed continuous shooting for capturing fast action
Getting Started with Your Canon Rebel SL1

Embarking on your journey with a new digital camera can be both exciting and overwhelming. This section will guide you through the essential steps to set up your device and start capturing beautiful images with ease. By following these initial instructions, you’ll quickly become familiar with your camera’s features and functions.
Unpacking and Assembling Your Camera

Before you begin using your new device, it’s important to properly unpack and assemble it. Here’s how to get started:
- Carefully remove the camera and accessories from the packaging.
- Attach the lens to the camera body by aligning the mounting dots and twisting it gently until it clicks into place.
- Insert the battery into the compartment, making sure it is oriented correctly as indicated by the markings.
- Install the memory card into its slot, ensuring it is firmly seated.
Basic Camera Setup

Once your camera is assembled, follow these steps to configure the basic settings:
- Power on the camera by pressing the main switch.
- Set the date and time by navigating to the menu and selecting the relevant option.
- Choose your preferred language for the menu and settings display.
- Adjust the default settings according to your preferences, such as image quality and shooting modes.
With these initial steps completed, you are now ready to explore the various features of your camera and begin capturing stunning photos. Enjoy your photography journey!
Essential Camera Settings and Adjustments
Understanding and mastering key camera settings is crucial for achieving desired photographic results. These fundamental adjustments allow you to control exposure, focus, and overall image quality, ensuring that each shot aligns with your creative vision. This guide explores the essential settings and how to effectively fine-tune them for various shooting scenarios.
Exposure Settings
Exposure is a primary element that determines the brightness or darkness of an image. To manage exposure, focus on three critical aspects: aperture, shutter speed, and ISO. The aperture controls the amount of light entering the lens and affects the depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-number) allows more light and creates a shallow depth of field, while a narrower aperture (higher f-number) lets in less light and increases the depth of field. Shutter speed dictates how long the camera’s shutter remains open. Faster speeds capture sharp details, whereas slower speeds can introduce motion blur. Lastly, ISO adjusts the camera’s sensitivity to light. Higher ISO values are useful in low-light conditions but may introduce noise or graininess to the image.
Focus and White Balance

Proper focus ensures that your subject appears sharp and clear. You can choose between different focusing modes, such as single-point, multi-point, or automatic, depending on the scene and subject movement. Additionally, adjusting the white balance is essential for accurate color representation. Different lighting conditions, such as daylight, tungsten, or fluorescent, affect how colors are rendered in your photos. Set the white balance according to the lighting environment to maintain natural colors and avoid unwanted color casts.
Tips for Optimal Photo Quality

Achieving the best possible photo quality involves understanding and mastering various settings and techniques. By making slight adjustments and being mindful of certain aspects, you can significantly enhance the clarity, detail, and overall appearance of your images.
Focus and Sharpness

Ensuring that your images are sharp and well-focused is essential for capturing detailed and clear photos. Consider the following:
- Auto vs. Manual Focus: Use automatic focus for quick shots, but switch to manual focus when precision is needed.
- Avoiding Camera Shake: Use a tripod or stabilize your camera to prevent blurring caused by movement.
- Aperture Settings: A smaller aperture (higher f-stop) increases depth of field, ensuring more of the scene is in focus.
Lighting and Exposure
Proper lighting and exposure are key to producing vibrant and well-balanced images. Here are some tips:
- Natural Light: Whenever possible, utilize natural light, positioning your subject to make the most of it.
- Exposure Settings: Adjust your exposure settings to prevent overexposure in bright conditions or underexposure in darker environments.
- ISO Sensitivity: Use a lower ISO for bright conditions to reduce noise and a higher ISO in low light to maintain exposure without sacrificing too much detail.
By carefully considering these factors, you can consistently produce high-quality photos that capture your vision with clarity and precision.
Understanding Camera Modes and Functions
Mastering the various modes and functions of your digital camera is essential for capturing high-quality images in different scenarios. Each mode is designed to optimize camera settings based on the subject matter, lighting conditions, and the desired outcome. Familiarizing yourself with these settings will allow you to take full control of your photography, whether you’re shooting landscapes, portraits, or action shots.
The camera provides several modes that cater to different shooting needs. These modes adjust settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO to suit specific conditions. Below is a breakdown of the most commonly used camera modes and their applications.
- Auto Mode: This mode is perfect for beginners or when you need a quick shot without worrying about settings. The camera automatically adjusts all the settings to produce a well-exposed image.
- Portrait Mode: Ideal for capturing people, this mode optimizes settings to create a shallow depth of field, making the subject stand out against a softly blurred background.
- Landscape Mode: Best used for wide scenes, this mode enhances depth of field to ensure that both foreground and background elements remain in sharp focus.
- Sports Mode: Designed for fast-moving subjects, this mode increases the shutter speed to freeze action, reducing blur in your images.
- Night Mode: This mode is tailored for low-light situations, often using a slower shutter speed and higher ISO to capture details in dimly lit environments.
In addition to these preset modes, your camera offers more advanced functions for photographers who wish to have greater control over their shots.
- Aperture Priority: Allows you to manually set the aperture while the camera adjusts the shutter speed. This mode is useful when you want to control the depth of field.
- Shutter Priority: Enables you to select the shutter speed, with the camera automatically adjusting the aperture. Use this mode when you need to control motion blur.
- Manual Mode: Gives you full control over both aperture and shutter speed, allowing for precise adjustments to achieve the desired exposure.
Understanding these modes and functions will empower you to take better photographs, tailored to the specific conditions and creative goals of your shoot.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting Guide
Proper care and timely issue resolution are essential for ensuring your camera operates smoothly and delivers optimal performance over time. This section offers guidance on routine upkeep practices and strategies to address common problems you might encounter. By following these recommendations, you can extend the longevity of your equipment and maintain its functionality.
Regular Cleaning: Keep the lens and body clean to prevent dust and debris from affecting image quality or causing operational issues. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to gently wipe down the external surfaces, and a blower or specialized brush to remove particles from the lens. For the sensor, use recommended cleaning tools and follow precise instructions to avoid damage.
Battery Care: Ensure your battery is charged regularly and stored properly when not in use. Avoid exposing it to extreme temperatures, which can reduce its lifespan. If the battery drains faster than expected, try a full discharge and recharge cycle to recalibrate the power levels.
Memory Card Maintenance: Format your memory card in the camera periodically to maintain optimal performance. Always turn off the camera before removing the card to prevent data corruption. If you encounter errors while accessing files, use a computer to run a disk check or consider using a new card.
Dealing with Errors: If you see an error message, refer to the corresponding error code in your device’s guide to diagnose the issue. Common problems may include lens errors, focus issues, or problems with the memory card. Restarting the device or resetting it to factory settings can often resolve these issues.
Firmware Updates: Regularly check for software updates to ensure your device is running the latest version. Updates can fix bugs, improve performance, and add new features. Follow the update instructions carefully to avoid interruptions during the process.
By adhering to these maintenance tips and troubleshooting methods, you can ensure your camera remains reliable and continues to produce high-quality images. For persistent or complex issues, seeking professional service may be necessary.
Exploring Advanced Photography Techniques

Diving into the realm of advanced photography allows you to unlock your camera’s full potential, transforming ordinary shots into extraordinary works of art. By mastering a variety of sophisticated techniques, photographers can enhance their creativity, capture dynamic compositions, and achieve professional-level results.
Mastering Exposure for Creative Control
Understanding exposure is crucial for taking control of your photographs. Exposure determines how light or dark an image will appear, and mastering it allows you to create specific moods or highlight particular details. The three main elements of exposure–aperture, shutter speed, and ISO–can be adjusted to achieve the desired effect.
- Aperture: Controls the depth of field, affecting how much of the image is in focus. A wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, isolating subjects against a blurred background, while a smaller aperture (higher f-number) increases the focus area.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how motion is captured. Faster shutter speeds freeze action, ideal for fast-moving subjects, whereas slower shutter speeds introduce motion blur, conveying a sense of movement.
- ISO: Adjusts the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO settings are perfect for bright conditions, producing cleaner images, while higher ISO settings are useful in low light, although they may introduce noise.
Exploring Advanced Composition Techniques
Advanced composition techniques go beyond the basics of framing and perspective, enabling you to craft visually compelling images that tell a story. Techniques such as leading lines, symmetry, and the rule of thirds can significantly enhance the impact of your photos.
- Leading Lines: Use natural or man-made lines within the scene to guide the viewer’s eye towards the main subject. This technique can create depth and draw attention to focal points.
- Symmetry and Patterns: Incorporating symmetry and patterns can create harmony and balance in your images. Look for reflections, repeating elements, or mirrored compositions to add visual interest.
- Rule of Thirds: Divide your frame into nine equal parts and position the key elements along these lines or at their intersections. This off-center placement often results in a more dynamic and engaging composition.
By experimenting with these advanced techniques, photographers can elevate their work, turning everyday scenes into powerful visual narratives.