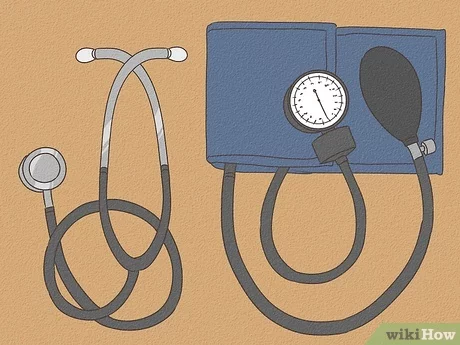
Understanding how to accurately assess your arterial health is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. One of the most reliable methods involves a traditional device that has been trusted for decades by healthcare professionals. This tool, though simple in design, requires proper technique and knowledge to ensure correct results.
In this guide, we will walk you through the step-by-step process of using this classic tool. We will cover everything from preparing the equipment and positioning it correctly to interpreting the readings with precision. By following these guidelines, you will gain the confidence needed to effectively monitor your cardiovascular health.
Whether you are a healthcare professional or someone looking to manage their own health more proactively, mastering this skill is invaluable. With careful attention to detail and practice, you will be able to obtain accurate measurements that are essential for making informed health decisions.
Understanding Manual Blood Pressure Cuffs
Grasping the basics of traditional devices used to measure the force of circulating fluid against vessel walls is crucial for accurate readings. These instruments are often relied upon in medical settings for their precision and reliability. They are composed of several key components that work together to help users obtain measurements and monitor cardiovascular health.
One of the main elements of these traditional devices is a flexible band that wraps around the upper arm. This band is inflated using a bulb, which increases the external force applied to the arm. The user then slowly releases the air while listening with a stethoscope to detect the sound changes in the arteries. The device’s dial or column helps to interpret these sounds into numerical values, which are crucial for understanding an individual’s cardiovascular condition.
Another vital part of understanding these devices is recognizing how they interact with the human body. Proper positioning of the arm, the fit of the band, and the technique used to inflate and deflate are all essential for obtaining an accurate measurement. It’s also important to be aware of potential sources of error, such as incorrect band size or placement, which can lead to inaccurate readings.
Learning how to properly use these traditional instruments not only ensures more precise results but also enhances one’s confidence in managing health assessments. Whether for home use or in clinical environments, mastering these skills is beneficial for anyone involved in health monitoring or patient care.
Components of a Manual Blood Pressure Cuff

A manual device for monitoring circulatory health is composed of several key parts, each playing a vital role in obtaining accurate readings. Understanding these components helps users operate the device more effectively and ensure proper maintenance. Let’s explore the various elements that make up this essential healthcare tool.
Main Elements
The main components typically include a measuring tool, an inflatable section, and a mechanism to control airflow. These parts work together to create the necessary conditions to gauge circulatory system performance accurately. The design and quality of these components are crucial for ensuring reliable and repeatable results.
Detailed Breakdown
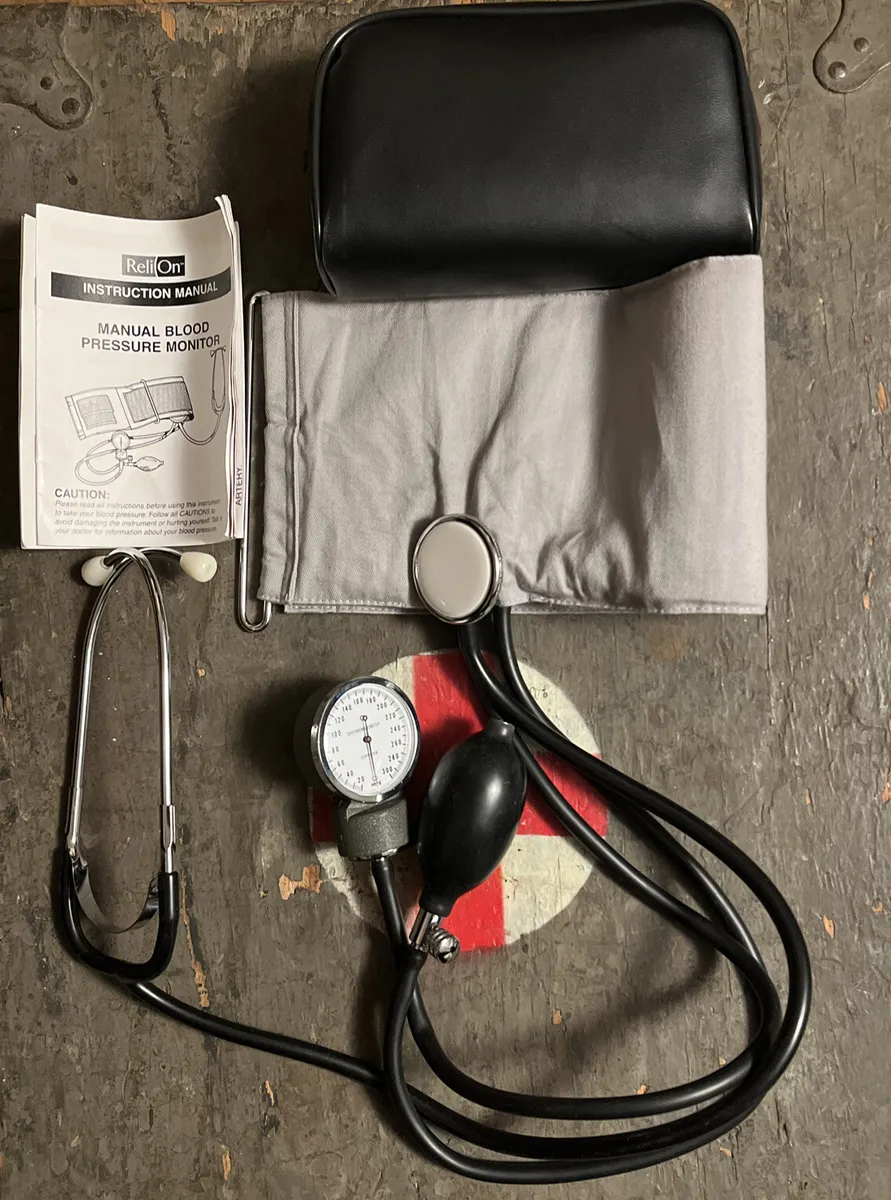
Below is a table outlining the key parts and their specific functions:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Aneroid Gauge | Displays the reading on a dial, indicating the force exerted within the vessels. |
| Inflatable Bladder | Wraps around the upper arm and expands when air is pumped in, compressing the vessels. |
| Bulb and Valve | Used to manually inflate the bladder and control the release of air to measure flow resistance. |
| Stethoscope | Listens to the sounds within the vessels, aiding in identifying key points during measurement. |
| Arm Wrap | Holds the inflatable section in place, ensuring consistent placement and accurate results. |
Each of these parts must be in good condition and used correctly to ensure the effectiveness of the device. Regular checks and maintenance are necessary to maintain the accuracy of readings and the longevity of the device.
How to Properly Position the Cuff
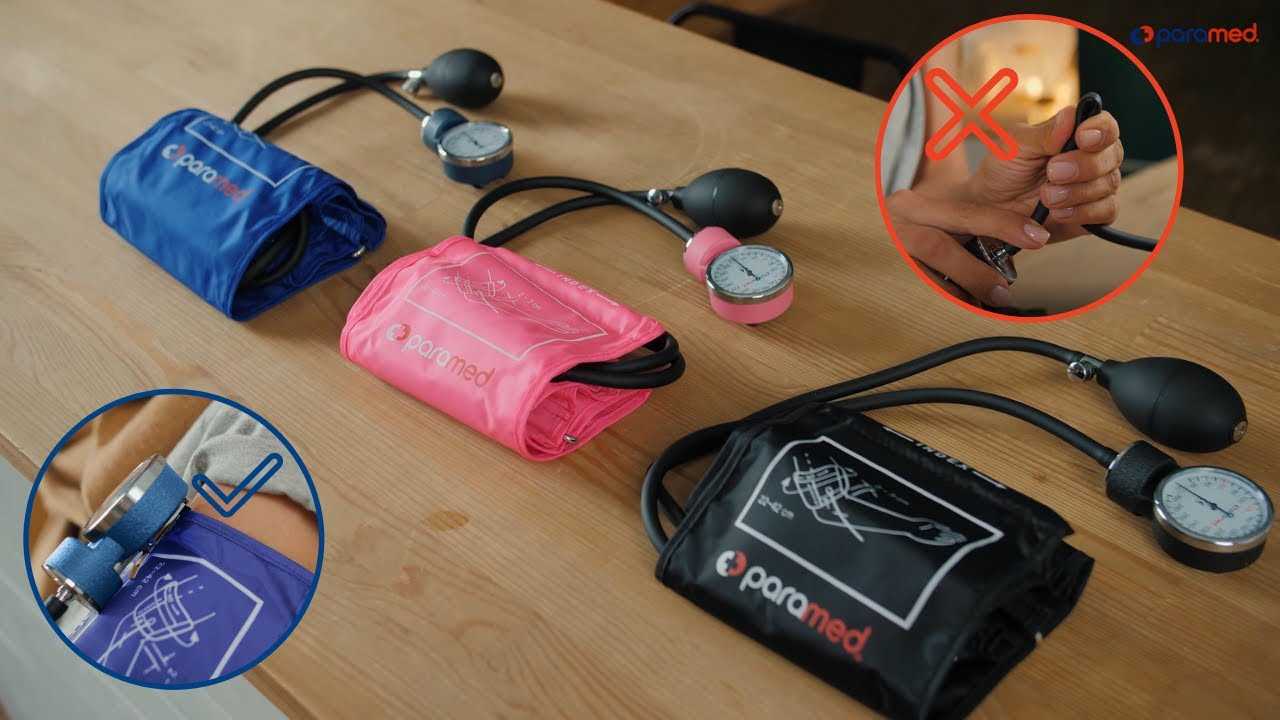

To ensure accurate readings, it’s crucial to place the measuring device correctly on the arm. Improper placement can lead to incorrect results, making it important to understand the proper technique. Follow these steps to ensure you’re getting the most reliable measurements possible.
Selecting the Right Arm and Position
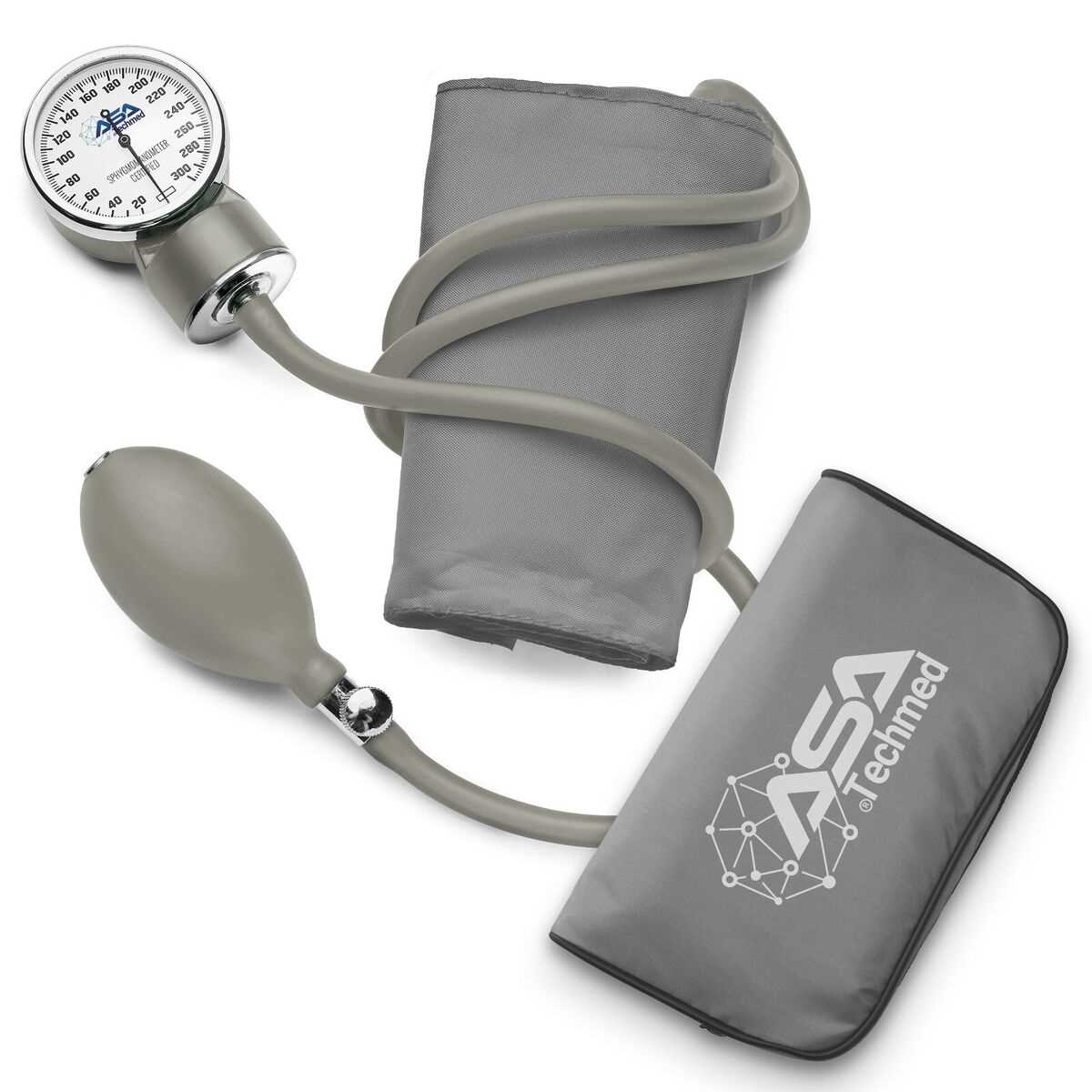
Begin by choosing an arm, preferably the one recommended by your healthcare provider. Generally, the non-dominant arm is preferred for consistency. Sit comfortably with your back supported and feet flat on the floor. Rest your arm on a flat surface, such as a table, at heart level. This positioning is key to obtaining an accurate reading.
Wrapping the Device Securely

Next, wrap the device around your upper arm, making sure it’s snug but not too tight. The lower edge should be about one inch above the elbow crease. Align the marking on the cuff with the artery, which typically runs down the middle of your arm. Ensure there is enough room to slip two fingers under the cuff to avoid excessive tightness, which can affect the measurement.
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Choose the appropriate arm for measurement. |
| 2 | Sit with your back supported and feet flat, resting your arm on a table at heart level. |
| 3 | Wrap the device around the upper arm, one inch above the elbow crease. |
| 4 | Ensure the device is snug but allows for two fingers to fit underneath. |
| 5 | Align the cuff marking with the artery for proper positioning. |
Step-by-Step Guide to Taking a Reading
Learning how to perform an accurate measurement at home is essential for maintaining awareness of your cardiovascular health. Following a series of simple steps, you can achieve precise results and monitor any changes effectively. This guide will help you understand the process from preparation to recording the final numbers.
Preparation Before the Measurement

- Find a quiet place where you can sit comfortably, free from distractions.
- Ensure you are seated with your feet flat on the floor and your back supported.
- Rest your arm on a flat surface, such as a table, so that it is level with your heart.
- Avoid consuming caffeine, alcohol, or engaging in strenuous activities 30 minutes before taking the reading.
Steps to Follow During the Measurement
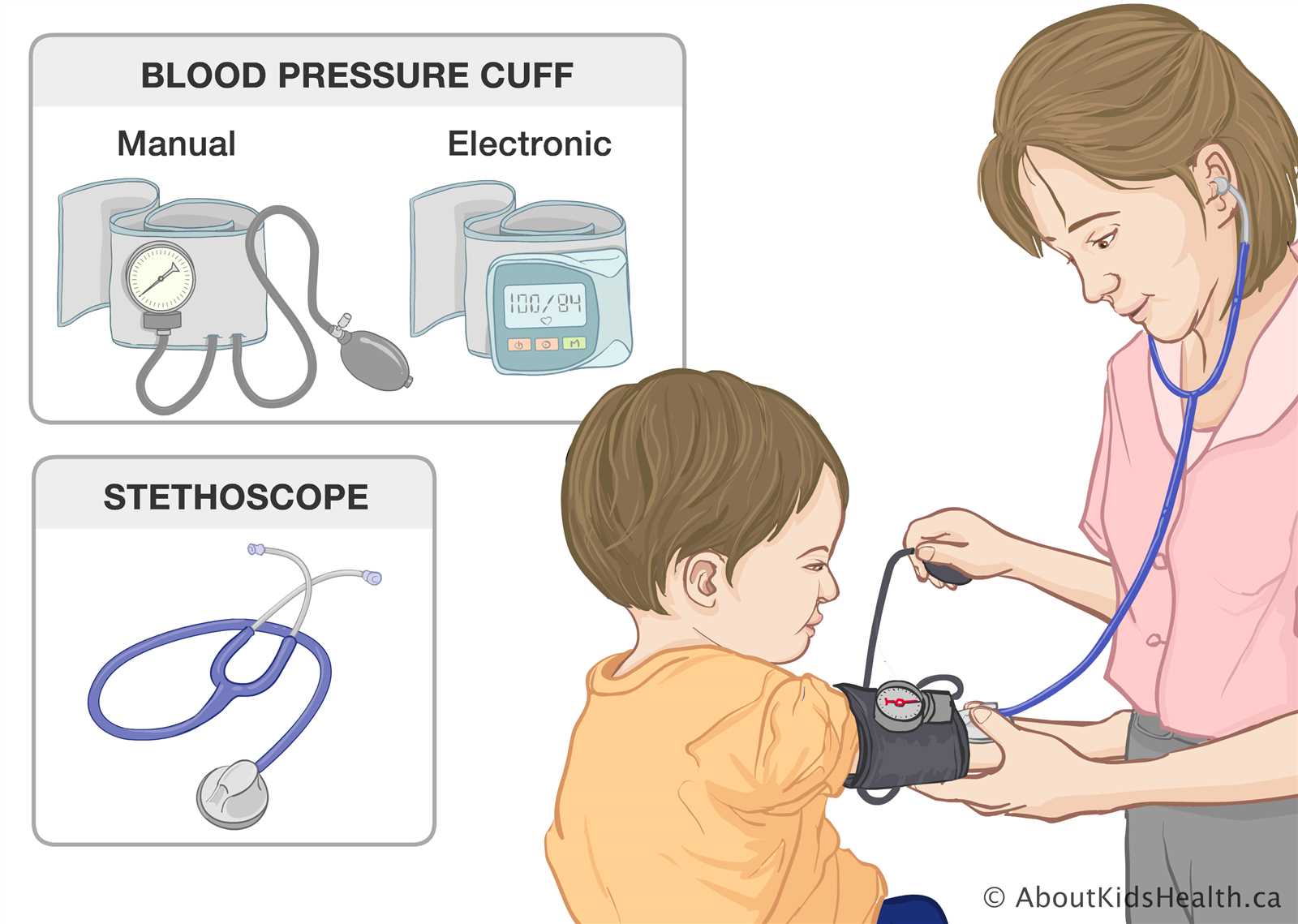
- Place the fabric loop around your upper arm, just above the elbow. Make sure it is snug but not too tight, allowing space for two fingers to slide underneath.
- Ensure the tubing from the device is aligned with the center of your inner arm, positioned over the brachial artery.
- Squeeze the rubber bulb to inflate the loop until it feels comfortably tight.
- Slowly release the valve to deflate, listening carefully for the initial thump and the final muffled beat.
Once you have completed the steps, note the numbers that appear. Record the results and compare them with previous readings to track any changes over time. Consistent monitoring will help you and your healthcare provider make informed decisions about your wellness plan.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
Accurate measurement of your vital signs is crucial for proper health management, but many individuals encounter difficulties due to frequent errors. Recognizing and correcting these errors can significantly enhance the reliability of your readings and ensure better health monitoring.
Incorrect Placement
One of the most common issues is improper placement of the measuring device. Ensuring it is positioned correctly on the arm is essential for accurate results. Make sure the device is placed at heart level and the tubing is not twisted or pinched. Avoid positioning the device too loosely or too tightly, as either can affect the accuracy.
Improper Preparation
Another mistake is failing to prepare properly before taking measurements. Ensure you are in a calm state and have rested for a few minutes before starting. Avoid measuring after physical activity or caffeine consumption, as these factors can skew the results. Following a consistent routine will help maintain accuracy.
By addressing these common errors, you can improve the reliability of your health monitoring and gain more accurate insights into your well-being.
Interpreting Your Blood Pressure Results

Understanding the readings from your measurement device is crucial for maintaining optimal health. These readings offer insight into your cardiovascular condition and help in assessing overall well-being. By analyzing these values, you can gain a clearer picture of your health status and determine if any action is necessary.
Systolic and diastolic values are the two key components of the measurement. The systolic value represents the force of blood against artery walls when the heart beats, while the diastolic value indicates the pressure during the heart’s rest phase. Both values are essential for evaluating your circulatory health.
Normal results typically fall within a specific range, whereas values outside this range may signal potential health concerns. Elevated readings could suggest conditions such as hypertension or other cardiovascular issues. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional if you encounter results that are unusually high or low.
Consistent monitoring and interpretation of these readings can help in managing and preventing health issues. Keep a record of your measurements to track any trends or changes over time, and share this information with your doctor for a comprehensive evaluation.
Maintaining and Storing Your Blood Pressure Cuff
Proper care and storage of your monitoring device are essential for ensuring its longevity and accuracy. By following a few simple guidelines, you can keep your instrument in optimal condition and ready for accurate readings.
To maintain your device, consider the following recommendations:
- Regularly inspect the device for any signs of wear or damage.
- Clean the device according to the manufacturer’s guidelines, typically using a damp cloth and mild soap.
- Avoid exposing the device to extreme temperatures, moisture, or direct sunlight, as these conditions can affect its functionality.
- Ensure that the hoses and connections are free of kinks and obstructions.
When it comes to storing your instrument, keep these tips in mind:
- Store the device in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight.
- Keep the device in its protective case or original packaging when not in use to prevent dust accumulation and physical damage.
- Avoid placing heavy objects on top of the device to prevent deformation.
- Regularly check the device for any signs of deterioration or malfunction, and address issues promptly.
By adhering to these maintenance and storage practices, you can ensure that your device remains reliable and accurate for years to come.