
In the ever-evolving world of audio production, having the right tools at your disposal can make all the difference. Whether you’re a seasoned broadcaster or just starting your journey into podcasting, understanding how to harness the full potential of your audio equipment is crucial for creating professional and polished soundscapes.
This guide is designed to walk you through the intricacies of one of the most versatile audio interfaces on the market today. From setting up your device to fine-tuning every detail of your sound, we aim to provide clear and concise directions, ensuring you can navigate each feature with confidence and ease.
As you explore the capabilities of this powerful device, you’ll discover how to streamline your workflow, enhance your recordings, and ultimately, produce high-quality audio content. With practical tips and step-by-step instructions, this resource is your key to unlocking the full potential of your sound equipment.
Getting Started with Your Audio Production Console
Welcome to your new journey in audio production. This guide is designed to help you set up and begin using your advanced audio interface, allowing you to capture and mix sound with ease. Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced user, this section will cover the essentials needed to get you started on creating professional-quality audio.
Initial Setup
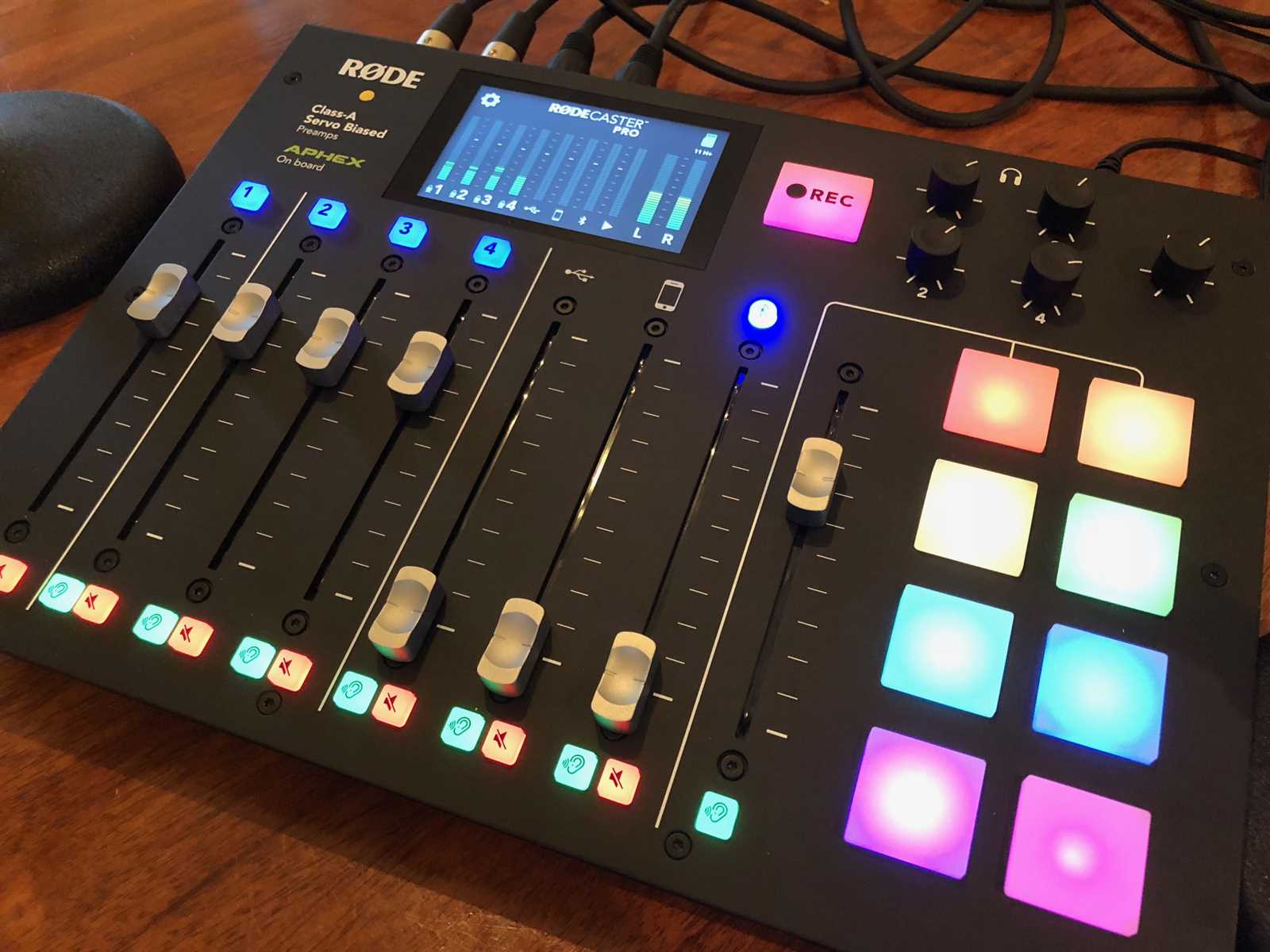
Start by connecting your console to a power source and turning it on. Ensure that all necessary cables, such as microphones and headphones, are properly connected. Familiarize yourself with the control panel and various inputs and outputs available on the device.
Basic Configuration
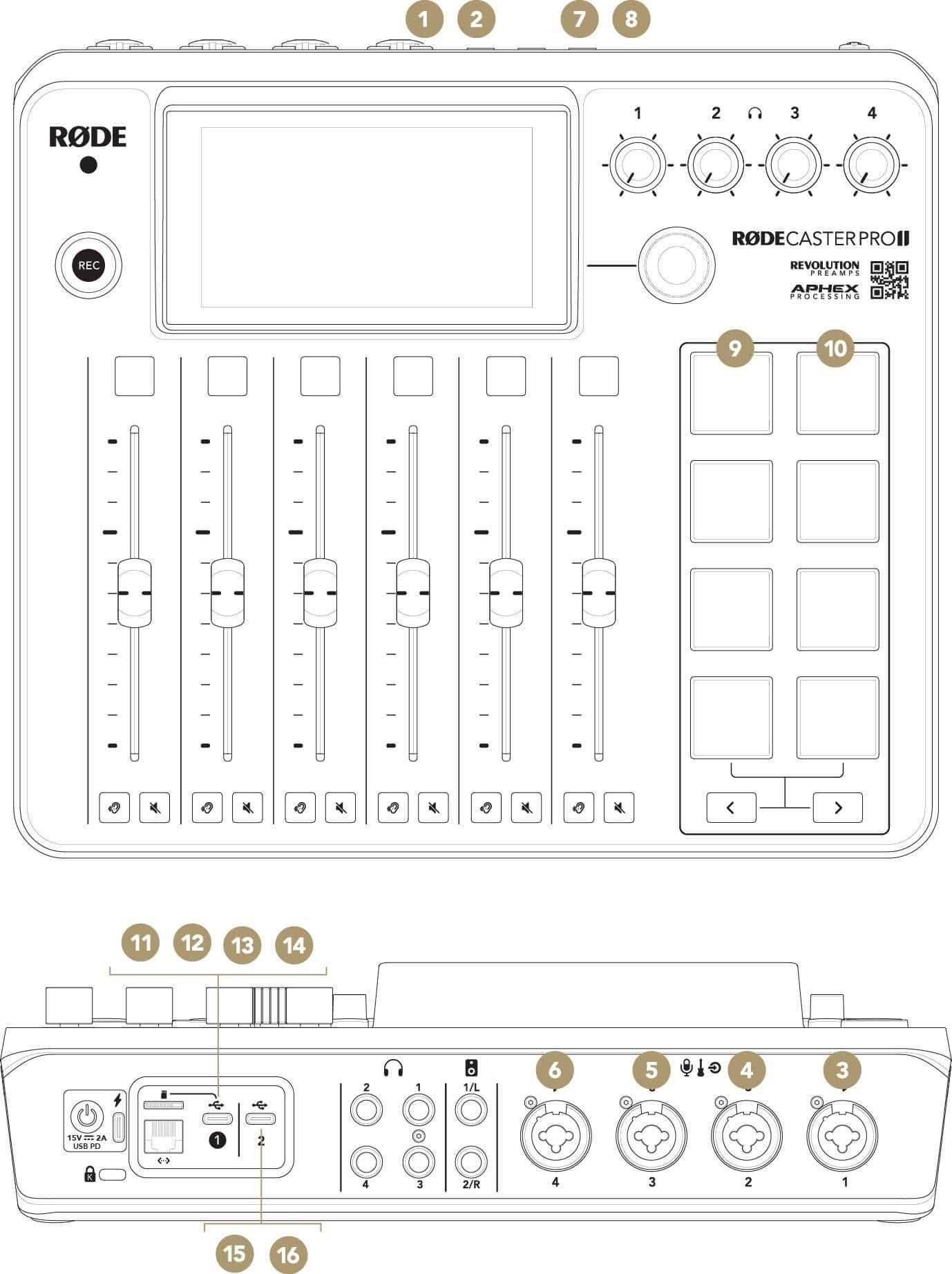
Once powered up, navigate through the menu to configure basic settings like audio levels, input sources, and output destinations. Take time to explore the different features and options available, as they will play a crucial role in shaping your recording experience. Don’t forget to perform a soundcheck to verify that everything is functioning as expected.
Understanding the Device’s Main Features
In this section, we explore the core capabilities that make this audio workstation an essential tool for creators. With a focus on delivering high-quality sound, this equipment integrates various functions tailored for seamless audio production. Whether you’re recording podcasts, live streams, or other audio content, these features are designed to enhance the creative process and simplify the workflow.
The multi-channel mixer is at the heart of the device, allowing you to balance and adjust different audio sources effortlessly. This feature ensures that each input can be fine-tuned to achieve the perfect mix, giving you full control over the audio environment.
Another key component is the integrated sound pads, which provide instant access to pre-recorded audio, sound effects, or music. These pads are customizable, making it easy to add a personal touch to your recordings or live sessions with just a press of a button.
One of the standout features is the built-in audio processing, which includes tools like compression, equalization, and noise gate. These tools help to polish the audio in real-time, ensuring professional-grade sound without the need for extensive post-production.
The device also supports multi-track recording, allowing each input to be recorded separately. This feature is particularly valuable for post-production, as it enables detailed editing and refinement of individual tracks.
For seamless integration with other equipment, the device offers multiple connectivity options. This includes USB interfaces, Bluetooth connectivity, and various input/output ports, making it versatile enough to fit into any existing setup.
Overall, the device’s features are designed to offer a comprehensive solution for audio content creation, balancing ease of use with powerful tools to enhance your projects.
Setting Up for Optimal Audio Quality
Achieving high-quality sound requires careful consideration of various factors in the audio setup process. From ensuring proper connections to configuring settings, every detail plays a crucial role in delivering clear, professional-grade audio.
- Microphone Placement: Position your microphone at an appropriate distance from the sound source to capture clear and consistent audio. Experiment with angles and distances to find the optimal spot.
- Input Levels: Adjust the input levels to prevent distortion. Set the gain so that the audio peaks just below the clipping threshold. This balance helps maintain clarity and avoids unwanted noise.
- Noise Reduction: Minimize background noise by selecting a quiet environment and using noise gates or filters. Ensuring minimal interference will enhance the overall audio quality.
- Equalization: Fine-tune the frequency response by applying EQ adjustments. Boost or cut specific frequencies to enhance the natural tone of your recording, tailored to the voice or instrument.
- Monitor Headphones: Use high-quality, closed-back headphones for monitoring. This helps detect any issues during the recording process and ensures accurate sound reproduction.
- Recording Environment: Optimize the recording space by adding soundproofing materials or acoustic panels. Reducing echo and reverberation will contribute significantly to the clarity of the recording.
By carefully setting up each element, you can significantly improve the audio output, creating a more polished and professional sound.
Recording and Managing Your First Podcast
Embarking on your podcasting journey is an exciting adventure filled with creativity and innovation. This guide will walk you through the fundamental steps of capturing your first episode and organizing your recordings effectively, ensuring your content is ready to reach listeners worldwide.
Setting Up for Success
Before hitting the record button, it’s crucial to create an environment conducive to clear and professional audio quality. Choose a quiet location, minimize background noise, and ensure your microphone is positioned correctly. Testing your equipment and adjusting levels beforehand can prevent potential issues during recording.
Recording Your Episode
With your setup in place, you can now begin recording your podcast. Focus on maintaining a consistent tone and pace, making sure your content flows naturally. Remember to engage with your audience as if they were right in front of you. If possible, record multiple takes of challenging sections, so you have options during the editing phase.
Once your recording is complete, save your work in an organized manner. Label your files clearly to avoid confusion later. Consider keeping backups to protect against data loss.
Managing and Editing Your Content
Post-recording, your next step is to edit your content. Trim any unnecessary pauses or errors, and consider enhancing the audio with effects if needed. Organize your segments logically, ensuring a smooth transition from one topic to the next. Take this opportunity to add any intro or outro music to give your podcast a polished feel.
After finalizing your edits, export your podcast in the desired format. Ensure your file is optimized for the platform you intend to publish on. Proper file management at this stage will streamline your future episodes, allowing you to focus more on content creation and less on technicalities.
Advanced Audio Processing Techniques
Understanding and mastering advanced audio processing techniques is crucial for achieving professional sound quality in any production. These techniques allow for refined control over sound, enhancing clarity, balance, and depth in recordings.
Dynamic Range Compression

Compression is essential for managing the dynamic range of audio. It reduces the difference between the loudest and quietest parts of a track, resulting in a more balanced and polished sound.
- Threshold: Determines the level at which compression starts to take effect.
- Ratio: Controls the amount of compression applied once the threshold is exceeded.
- Attack: Sets how quickly the compressor responds to signals above the threshold.
- Release: Adjusts the time it takes for the compressor to stop affecting the signal after it drops below the threshold.
Equalization (EQ)
EQ is used to shape the tonal characteristics of audio. By adjusting specific frequency ranges, you can emphasize or reduce certain elements within a sound.
- High-Pass Filter: Removes low-frequency noise or rumble by allowing only frequencies above a certain point to pass.
- Low-Pass Filter: Cuts high-frequency content, often used to soften harshness or reduce hiss.
- Parametric EQ: Provides precise control over frequency bands, allowing for fine-tuning of specific elements within the audio.
Mastering these techniques is key to producing clear, dynamic, and professional-sounding audio, whether in live recordings or post-production settings.
Integrating External Equipment and Software
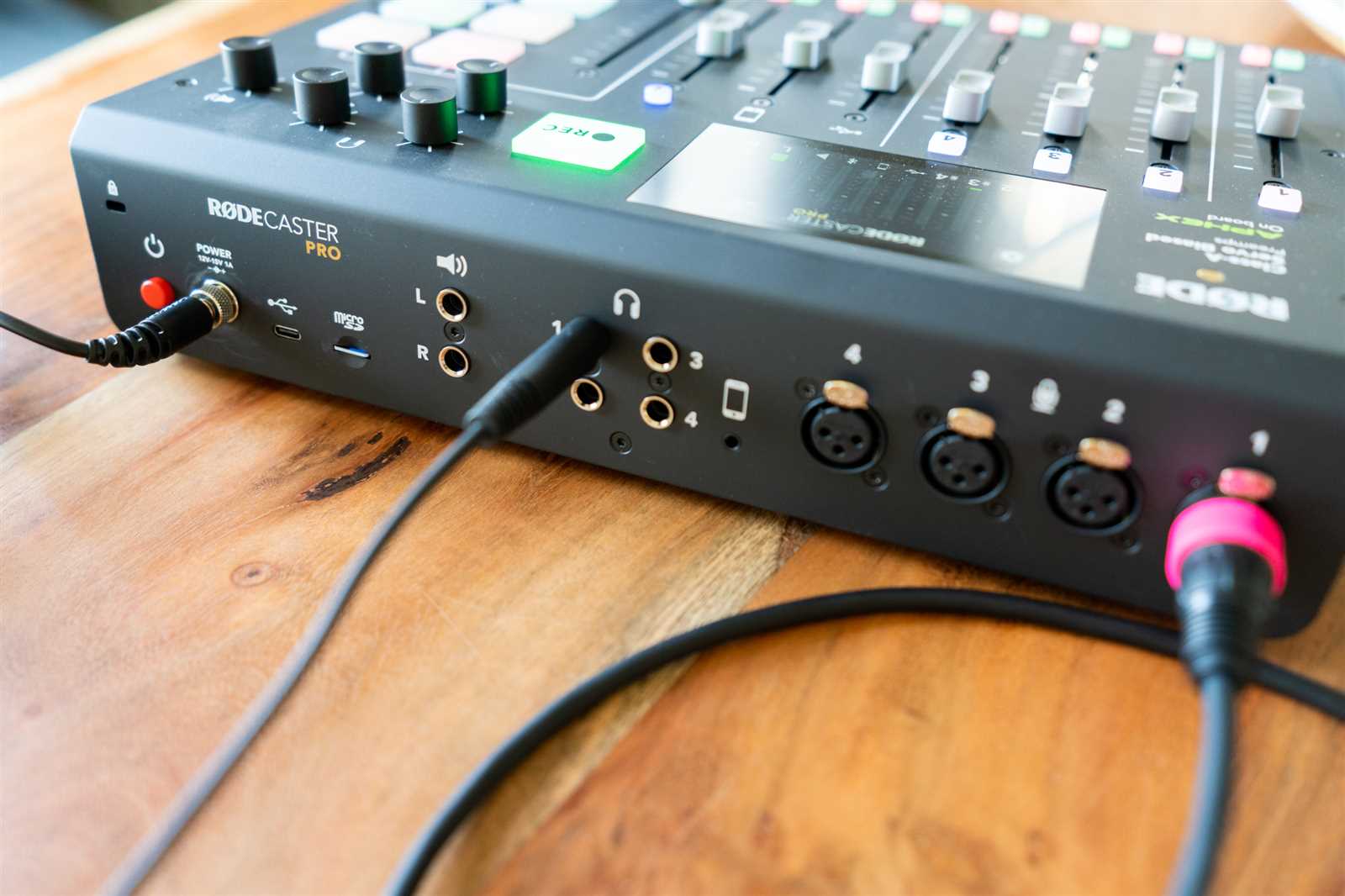

Incorporating external devices and applications into your audio setup can significantly enhance its functionality and versatility. This process involves connecting various hardware components and software tools to expand the capabilities of your recording or broadcasting system. Proper integration ensures seamless operation and enables you to leverage additional features for a more dynamic and professional performance.
Connecting External Hardware
To integrate external hardware, start by identifying the input and output ports available on your main device. Common connections include USB ports, XLR inputs, and line-level inputs. Use appropriate cables and adapters to connect microphones, instruments, or other audio sources. Ensure that each connection is secure and properly configured in your system’s settings to achieve optimal performance and sound quality.
Integrating Software Applications
Software integration involves linking digital tools that enhance audio processing, mixing, or recording. Install the necessary drivers and software packages on your computer or other devices. Configure your system to recognize these applications and route audio signals accordingly. By setting up proper communication between your main unit and software tools, you can take advantage of advanced features such as virtual effects, multi-track recording, and real-time editing.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Addressing technical difficulties can often be straightforward if approached methodically. By systematically identifying and resolving common problems, users can quickly restore functionality and avoid unnecessary disruptions. This section provides guidance on solving frequent issues encountered with audio equipment, ensuring a smoother user experience.
Audio Output Problems
If you are experiencing issues with audio output, such as no sound or distorted audio, follow these steps to diagnose and correct the problem:
| Problem | Solution |
|---|---|
| No sound | Check if the volume is turned up and not muted. Ensure that all cables are securely connected and that the correct audio source is selected. |
| Distorted audio | Verify that the audio levels are not set too high. Check for any loose or damaged cables that could affect sound quality. |
Connectivity Issues
Connectivity problems can hinder the functionality of your device. Here’s how to resolve common connectivity issues:
| Issue | Resolution |
|---|---|
| Device not recognized | Ensure that all connections are properly made. Restart the device and check for any required drivers or software updates. |
| Unstable connection | Make sure cables are firmly connected and not damaged. Test with different cables or ports to identify the source of instability. |